
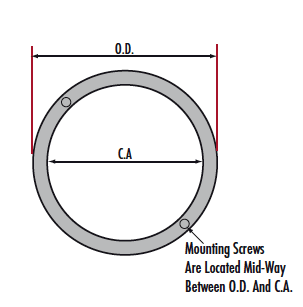
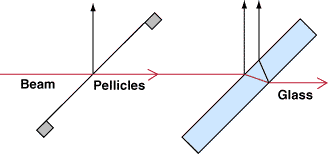
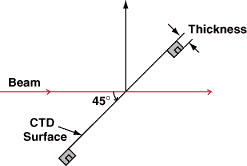
Infrared (IR) Pellicle Beamsplitters feature thin nitrocellulose beamsplitting membranes mounted in aluminum frames and are designed to have a 45R/55T beamsplitting ratio from 3 - 5µm. The thin nitrocellulose membranes eliminate second surface reflections and beam displacement while minimizing changes in the optical path length. The aluminum frames feature mounting holes on the underside of the frame to facilitate mounting and integration into OEM systems. Infrared (IR) Pellicle Beamsplitters are ideal for MWIR applications including MWIR imaging, infrared spectroscopy, flame detection, and general use with infrared detectors.
Note: The nitrocellulose membrane of these beamsplitters is very thin and fragile. The membrane should not be touched and cleaning should be done only with air. We recommend using an air blower as the force from compressed air may damage the membrane.
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2023 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act